A Web Design Glossary: 22 Common Terms Explained
Dennis Kardys Head of Design & Development#Industry Insights, #Design Advice, #Digital Strategy

We share and define 22 web design terms that are commonly used in the industry.
One of the hardest parts of shifting to a career in the web or product world is the unbelievable amount of industry jargon woven into daily dialogue. To an outsider, the volume of terms and acronyms you need to know to keep up with conversation can be totally mind-numbing. If tech-speak is throwing you for a loop and you're struggling to get familiarized with all the lingo, here's a glossary of some of the more commonly used web design terms to the rescue!
Agile
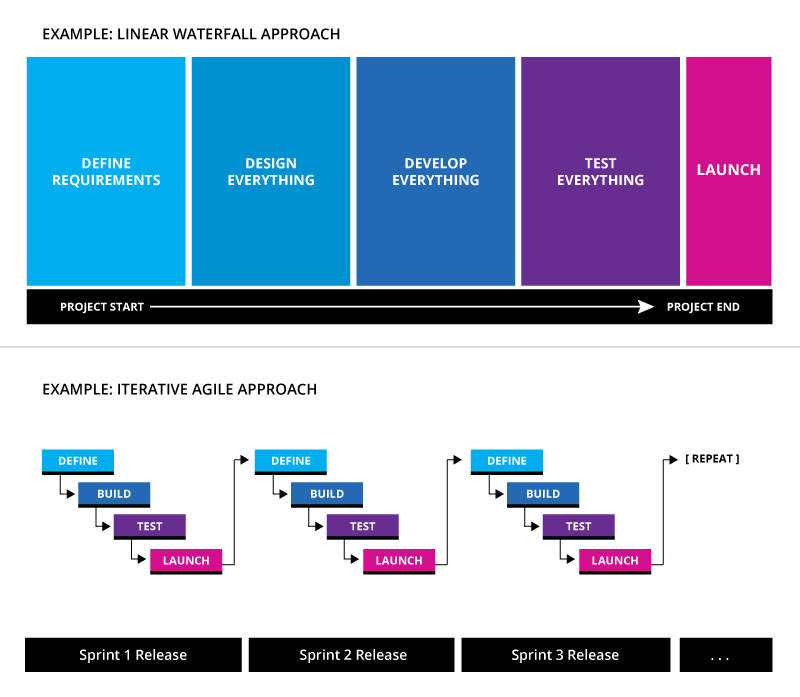
The term "agile" refers to an iterative, incremental method of managing design and development. In an agile workflow, requirements evolve from sprint to sprint, and teams work in a collaborative structure. In an agile project, code is shipped and features are released continually, unlike in a fixed-bid, fixed-timeline, single release waterfall project.
API
An API (Application Programming Interface) is a mechanism that allows different systems to communicate. It provides a method of accessing or manipulating data from a system, usually provided by the system's implementors. A "system" could be anything. Examples include applications like PayPal, Shopify, and Salesforce, but it could also be a custom application that stores shipping rules, product inventory and prices. Developers create APIs so that data that exists in their system can be made available in other places. For example, if you want data that exists in your CRM to display on your website, your website developer would check to see if there is an API that would allow the information to be accessed. If the API exists, the website developer can write code that will display it on the site. They could potentially also use the API to push information from the website into the other system.
Back-End Development (Application Engineers)
Back-end developers are engineers who take working proofs of concepts (prototypes) and write all the code that makes them fully functional and populated with real data. For websites, a back-end developer will connect your website to some sort of content management system that lets content owners manage and update website content themselves. They will also build in any integrations that pull or push data to and from other sources, such as a database or a third party system. A back end-developer will specialize in one or more programming languages.
CMS
A CMS (Content Management System) is a platform where people who manage an organization's website can log in to edit and publish content. Within a content management system, site editors can do things like control the site navigation, add or update text content, upload images, and build new pages. Examples of popular CMS's include: Wordpress, Joomla, Sitecore, Episerver, Ektron, and Umbraco.
CRM
A CRM (Customer Relationship Management) system is a tool used to manage customer information. It will typically store things like customer contact information, customer status (lead, prospect, active customer), sales or service history, etc. Popular CRMs include Salesforce, Zoho and HubSpot.
Development Languages
There are many different development languages that back-end developers may use. Examples include: PHP, Rails, ASP, C#, C++, Python, and .NET. Similar to languages in the real world, each programming language has its own syntax and language rules.
Discovery
Discovery is a focused period where teams are dedicated to developing a deeper understanding of: a client, their business, their users, and all the context and restraints that surround current and future projects. In discovery, learning goes both ways. It's an opportunity for a web team to learn more about a client and their business, and for the client to learn more about the design and development process. The amount of time spent in discovery can vary depending on the activities planned and outcomes desired. A typical discovery might consist of 2-4 sequential full days of interviews, workshops and presentations onsite with a client. Or, in other scenarios, discovery might be an entire "learning" phase of a project.
Front End Development
Front-end developers write the code that controls how a website looks and interacts when it's displayed in a browser. The primary tools of a front-end developer include HTML (code that makes content render on a page), CSS (coded stylesheets that apply color, typography, style and layout to the HTML) and JavaScript (code that handles advanced interactivity). A front-end developer will also work with a handful of other frameworks that help expedite, enhance, and organize the coding process.
Inbound Marketing
Inbound marketing is a philosophy for attracting customers and growing your target audience through the production and sharing of useful, relevant information. Blogging, producing videos, and publishing eBooks are all examples of inbound marketing. This is to be contrasted with traditional outbound marketing techniques like email blasting, cold calling, and business self-promotion.
Marketing Automation
Marketing Automation Platforms (MAPs) are systems that help businesses automate interactions with current and prospective customers, usually with the end goal of being able to generate, track, and convert business leads. Marketing automation platforms are used to collect and manage information about your customers, send and manage email campaigns, and monitor website behavior and usage—often surrounding inbound marketing campaigns. Popular Marketing Automation platforms include: Hubspot, Marketo, Pardot, and Eloqua.
Prototypes
A prototype is a proof of concept used to evaluate a design idea. For example, rather than creating a static mock up of what a web page will look like and then asking stakeholders to "approve the design", a team might create a prototype that everyone can interact within the browser. This gives everyone a more realistic, interactive facsimile of the website to try out. Prototypes help teams test ideas and make necessary changes early on—before committing the effort, time and cost that go into building a fully functional product.
QA/QC
In the course of design and development, somebody needs to review all the work produced, verify that everything is built to spec, and ensure that there are no defects. This is the role of the Quality Assurance and Quality Control engineer. QA (Quality Assurance) refers to the process and standards that exist throughout the software development life-cycle. QC (Quality Control) refers to the action of performing tests to ensure quality at specific points during the production process.
Quantitative Research and Data
Quantitative data refers to any aggregated, measurable pieces of information. Typically, it refers to data (analytics) that reflects website/application traffic and usage. On its own, quantifiable data will provide information about what is happening on your website, but not why it's happening. Being able to quantify what's happening (or not happening) on your website can help you determine the best place to focus your UX research, design and development efforts.
Qualitative Research and Data
Qualitative data is information gained through direct observation or interviews with the people who use a product or system. Usability testing is a form of user research that generates qualitative insights. Whereas analytics and metrics may provide quantitative information about what's happening on your website, qualitative research will help you understand why you are seeing those results. Your qualitative insights will help you know what changes might improve things like conversion rate or user experience.
Roadmap
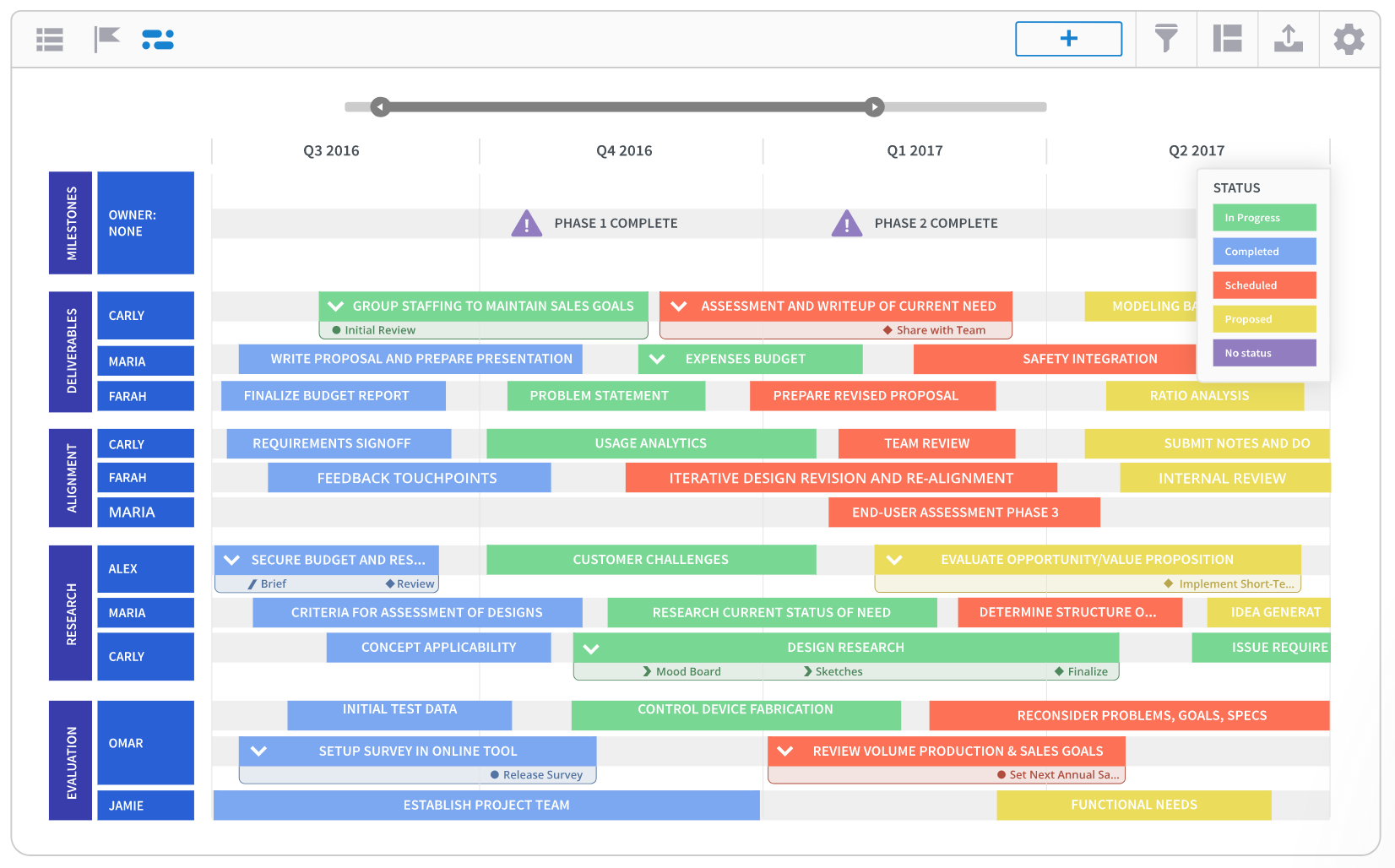
A roadmap is a living document that paints out planned strategic activities across a stretch of time. Roadmaps are used to help teams and stakeholders visualize the timeline of moving pieces that need to be aligned as part of big initiatives. A typical roadmap will display key project deadlines and feature releases, often tracked across months or quarters.
Sprints
A sprint is the determinate window of time a team has to successfully complete a chunk of work. Sprints are used to deliver design work, deploy code, and ship new features incrementally. Sprints help teams organize development tasks into manageable stand-alone pieces. Each team's individual sprint-cycle should reflect a specific interval of time. For example, a team in a 3-week sprint cycle will plan, execute on, complete and deliver work for testing every 3 weeks.
UAT
UAT stands for User Acceptance Testing. This is an incredibly misleading term as there are no "end users" actually involved (end users being real-world users within the target audience). The user in UAT refers to the client stakeholder team responsible for providing final sign off and approval that features are working as expected, prior to pushing them live.
UI Design
UI (User Interface) Design is the design of how things on screen look. Color, layout, typography, style, and animation effects all exist within the domain of UI design. UI designers will have a solid understanding of the principles of graphic design and website usability. It's not uncommon for web designers to have multiple areas of expertise, for example a web designer might be versed in both interface design and user experience or front end development.
Usability Testing
Usability testing involves sitting down with a user of a website, product, or application and observing what they do. This can be done in person, or remotely via screen share. A typical usability testing session combines a general interview with guided and unguided walkthroughs of the interface being tested. When guided, the tester will ask the user to complete a series of tasks and identify what things the user can do easily, and where the user encounters friction (has difficulty). When unguided, the user will take the lead in an open walkthrough of their thoughts and the tasks they would most naturally try to complete.
User Research
Any of a toolbox of techniques used to gather insights about people, their motivations, and their behavioral patterns—specifically as they pertain to interactions with products, websites or applications. User research can include a combination of quantitative and qualitative techniques.
UX
UX stands for user experience. User experience, as a discipline, is the application of design tools and techniques to uncover user goals and needs. This all works toward the goal of crafting products, applications, and systems that are useful, desirable, and easy for people to use. User experience is also used as an umbrella term to reflect the overall degree of satisfaction a person will have interacting with a product or website. Everything that impacts user satisfaction: how quickly a screen loads, how well-written and relevant content is, how easy it is for users to navigate or complete tasks all contribute to the overall user experience.
Waterfall
Waterfall is a linear project workflow where each step in the process happens in sequential phases. First planning, then design, then development, then testing, then deployment. In a waterfall project there is a series of handoffs; as each phase is completed it's passed to the next team in line until ultimately ending with a single, final release.
Whether you are shifting to a new career or hear these terms when working with other companies, this guide can be helpful in understanding the lingo during the conversation. Let us know in the comments if there are additional terms you've had to clarify.
Related Posts
Agile Research: Enhancing Web Projects with Ongoing Feedback
Agile research ensures your web project evolves with real-time insights for greater ROI and user satisfaction.

Accessibility Playbook Resources
Useful accessibility resources that are free for web designers, web developers, and content creators to help them build more inclusive websites.
Results Matter.
We design creative digital solutions that grow your business, strengthen your brand and engage your audience. Our team blends creativity with insights, analytics and technology to deliver beauty, function, accessibility and most of all, ROI. Do you have a project you want to discuss?
Like what you read?
Subscribe to our blog "Diagram Views" for the latest trends in web design, inbound marketing and mobile strategy.
